Module 2: Parallel Hardware and Software¶
Serial System¶
The traditional von Neumann architecture¶
CPU
Control unit
Arithmetic logic unit (ALU)
Memory
Input/Output (I/O)
Operating system¶
Process
Multitasking
Thread
Cache¶
Definition: A cache is a smaller, faster type of volatile computer memory that provides high-speed data access to the processor and stores frequently used computer programs, applications, and data.
Locality
Temporal locality
A memory location that is referenced once is likely to be referenced again soon.
Spatial locality
A memory location near the location that is referenced once is likely to be referenced again soon.
Leveled
L1, L2, L3, … from faster/smaller to slower/larger
Cache line
Cache address mapping
Cache hit/miss
Cache mapping
Direct mapping (temporal locality)
Select one cache line to store in the cache
A line of data can be stored in any cache line
Full associative mapping (spatial locality)
Select a block around the line of data and store the whole block in the cache
The whole cache is occupied by the block
A line of data can only be stored in one cache line
Set-associative mapping (both)
Split the cache into several sets
Select a block around the line of data and store the whole block in the cache
A set is occupied by the block
A line of data can only be stored in one cache line per set. Thus, there are the number of sets possible way to store the line of data.
Cache eviction policy
Virtual memory¶
Use secondary storage as an extension of main memory
Page - Fixed length block
Swapping - unused page moved to secondary storage
Virtual address
Page table - mapping from virtual address to physical address
Translation lookaside buffer (TLB) - cache for page table
Page fault - page not in memory
Instruction level parallelism (ILP)¶
Internal feature of a CPU to allow parallelism. Hardware dependant.
pipeline - unique subunit
multiple issue - replicated subunits
Thread level parallelism (TLP)¶
Parallel Hardware¶
Type of parallelism
data parallelism
task parallelism
Flynn’s taxonomy¶
Single instruction single data stream (SISD)
classic von Neumann
Single instruction multiple data (SIMD)
Vector processor
Dedicated vector processor
General CPUs with vector instructions
Intel SIMD intrinsics: MMX, SSE, AVX
GPUs single core (Graphical Processing Unit)
Multiple instruction multiple data stream (MIMD)
Types
shared-memory
distributed memory
Distributed-memory SIMD¶
interconnections
direct (nodes are connected by a single switch)
fully connected
hypercube
indirect (nodes are connected by multiple switches)
crossbar
omega network
Time to send a message
latency - preparation time
bandwidth - transfer time
\(time = latency + size/bandwidth\)
bisect width/bandwidth
Parallel Software¶
Focus on Single program multiple data (SPMD) programs
A single program is executed by multiple processes/threads/nodes
Each process/thread/node executes the same program
Each process/thread/node has its own data
Distributed-memory system¶
Communicating by message passing
The Message-Passing Interface (MPI) standard
MPICH
OpenMPI
Performance Model¶
Variables¶
Serial run-time \(T_{serial}\)
Parallel run-time \(T_{parallel}\)
Number of processes/threads/nodes \(p\)
Problem size \(N\)
Metrics¶
Speedup \(S = T_{serial}/T_{parallel}\)
Efficiency \(E = \frac{S}{p} = \frac{T_{serial}}{p \cdot T_{parallel}}\)
Relationships¶
Ideal
\(S = T_{serial}/T_{parallel} = p\)
With overhead
\(T_{parallel} = T_{serial}/p + T_{overhead}\)
\(S = T_{serial}/T_{parallel} < p\)
Amdahl’s law
Let \(f\) be the fraction of the program that can be parallelized
Then the speedup
\(S = \frac{1}{(1-f) + \frac{f}{p}}\)
Diminishing return
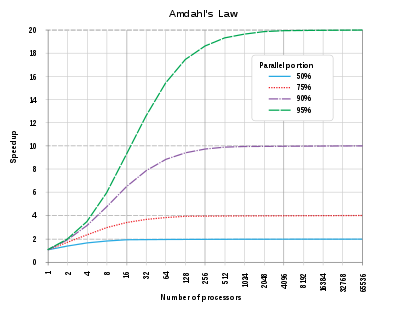
Scalability
strong scaling
Constant \(E\) with increasing \(p\) for a fixed \(N\)
plot:
\(E\) vs \(P\)
fixed \(N\)
Expect nearly flat line
weak
Constant \(E\) with increasing \(p\) for a fixed \(N/p\) ratio
plot:
\(E\) vs \(P\)
fixed \(N/p\)
Expect nearly flat line
Timing
Parallel Program Design¶
Foster’s methodology
Partition
Communication
Agglomeration
Mapping
Histogram example
code example available