Big Data For Data Science
Module 2: Data storage for Big Data
Xingang (Ian) Fang
Outline
Overview of data storage for big data
File systems/Storage services for big Data
NoSQL databases for big data
Overview
What we care most
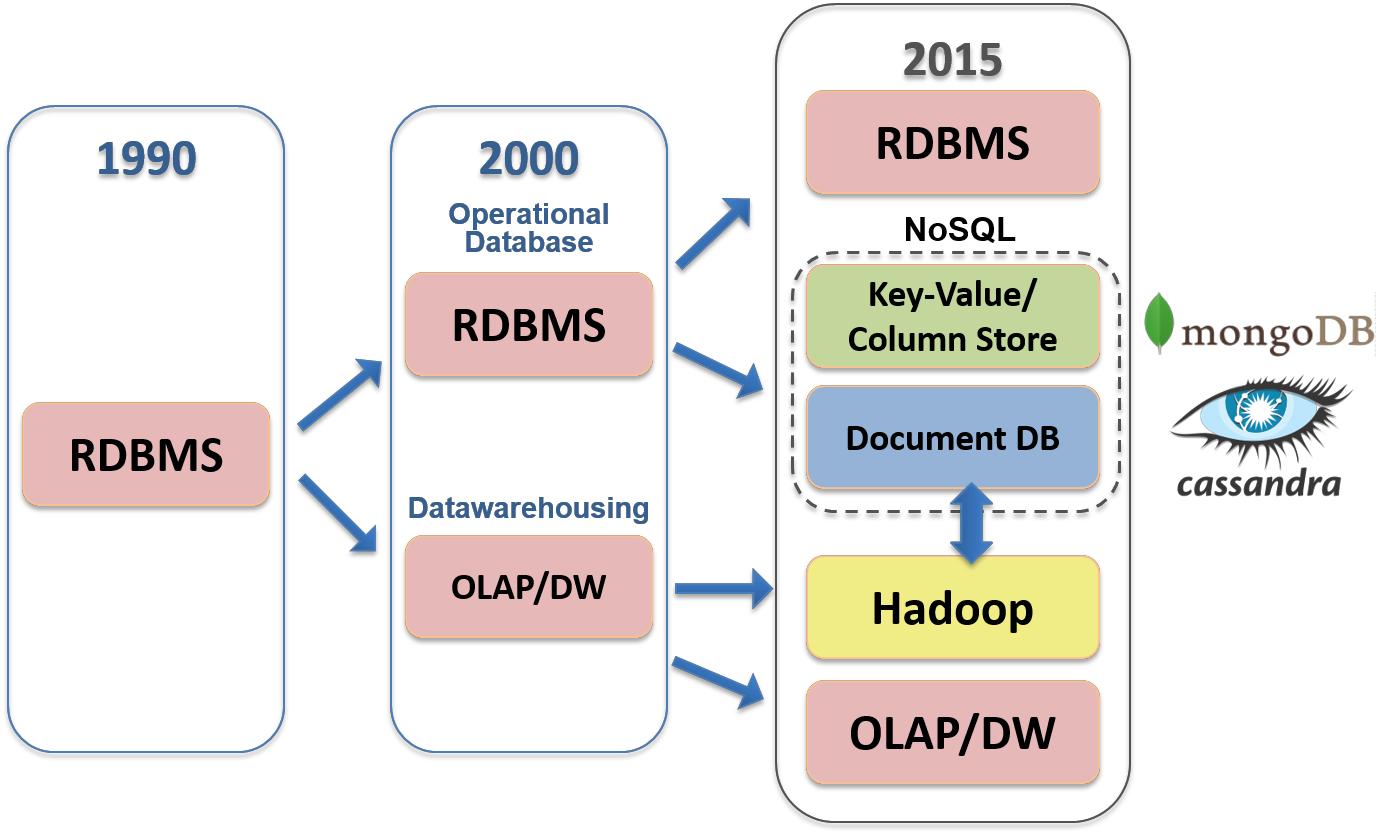
Traditional data storage vs Big data storage
Types
Distributed filesystem
Object store
NoSQL
What we care most?
📈Scalability - Volume
💰Cost - Volume
🚀Performance - Velocity, Volume
💪Robustness - Veracity
🗄Data organization and structure - Variety
Traditional vs Big Data Storage
Traditional
File system: unstructured data as files in directories
Relational Database: structured data as records in database
Big Data
Distributed file system: data organized as files
Object store: data organized as objects
NoSQL Database: data organized as records, documents, nodes, etc.
Three Types Of File Systems/Storage Services
Distributed filesystem
Flexibility to choose own infrastructure or cloud infrastructure
Performance in data processing
Good scalability
Best for analysis
Object store
Cloud with many storage classes to choose from
Infinite scalability
Flexibility (choice of services)
Cost effective - not owning hardware, lower price
Best for archiving, backup, etc.
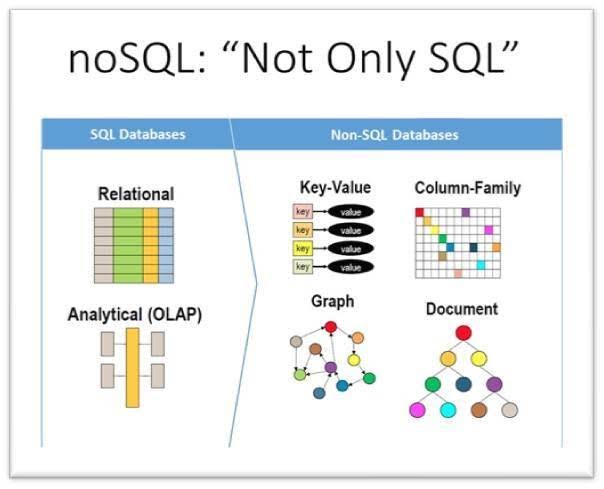
NoSQL
Not only SQL
Uniformed SQL like API for data handling
Some compatibility to relational database API
Structured and semi-structured data
Leave the data management to DBMS (database management system)
File systems/Storage services for big Data
Distributed file system
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
Commercial Cloud Storage Services
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS)
Google Cloud Storage Service
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
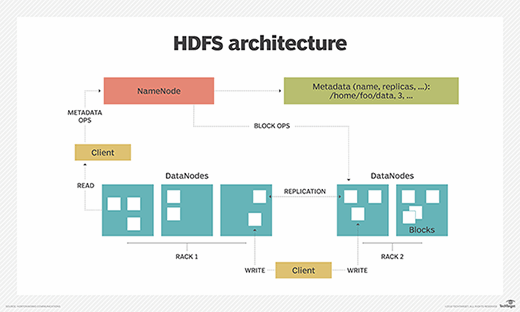
HDFS architecture and components
NameNode, DataNode
HDFS data organization
blocks
replication
rack awareness
HDFS operations
reading
writing
appending
deleting
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
Amazon S3
S3 storage classes (standard, infrequent access, glacier, etc.)
S3 data organization (buckets, objects, keys)
S3 operations (uploading, downloading, copying, deleting)
Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS)
Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS)
Overview of ADLS storage tiers (hot, cool, archive)
ADLS data organization (file system, directories, files)
ADLS operations (creating, reading, updating, deleting)
Google Cloud Storage Service
Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage classes (multi-regional, regional, nearline, coldline)
Google Cloud Storage data organization (buckets, objects, keys)
Google Cloud Storage operations (uploading, downloading, copying, deleting)
NoSQL databases for big data
Introduction to NoSQL databases
Types of NoSQL databases
Use cases of NoSQL databases
Introduction to NoSQL databases
Overview of the NoSQL database
NoSQL (not only SQL) databases, a.k.a non-relational databases
Designed to address the problem of relational databases
Especially when handling large volume of data
Flexibility, scalability, and availability
Characteristics of NoSQL databases
Advantages over traditional relational databases
Drawbacks compared to relational databases
Future of NoSQL databases
Characteristics of NoSQL databases
Most common characteristics of NoSQL databases are:
Non-Relational
Horizontal Scalability
High Availability
Distributed Architecture
Flexible Schema
Performance
Advantages over traditional relational databases
Handles both structured and semi-structured data
Higher scalability
Higher availability
Flexibility and versatility
Various solutions to fit the need
Flexible schema and deployment options
Features |
SQL |
NoSQL |
|---|---|---|
Model |
Relational |
Non-relational |
Schema |
Rigid |
Flexible |
Query language |
SQL |
DSL |
Scalability |
Vertical |
Horizontal |
Transactions* |
ACID |
BASE to ACID |
Integrity |
Strong |
Eventual to strong |
* “ACID vs. BASE: Comparison of Database Transaction Models”, https://phoenixnap.com/kb/acid-vs-base
Drawbacks compared to relational databases
Less mature transactional support
Less compatibility with legacy system
Limited query capability
Relaxed consistency/integrity
In trade to advantages
Flexible schema
Complex data organization
Complex relationships
Distributed
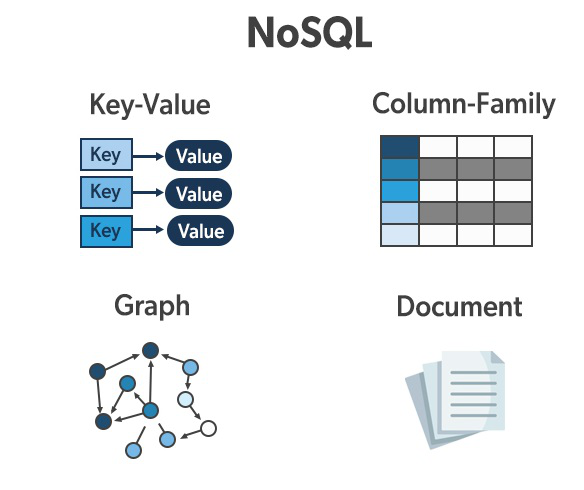
Types of NoSQL databases
Document-based databases (MongoDB, Couchbase)
Key-value databases (Redis, Amazon DynamoDB)
Column-family databases (Apache Cassandra, HBase, Google BigTable)
Graph databases (Neo4j, OrientDB)
Use cases of NoSQL databases
Overview of NoSQL databases use cases
Use cases for document-based NoSQL databases
Hierarchical organization
Unstructured and semi-structured data
Use cases for key-value NoSQL databases
Caching
Fast lookup
High availability
Use cases for column-family NoSQL databases
Horizontal scalability
Use cases for graph NoSQL databases
Graph modeling
Network modeling
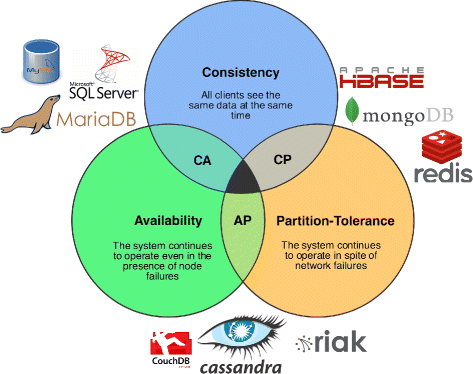
Credit: Lourenço, João Ricardo, et al. “Choosing the right NoSQL database for the job: a quality attribute evaluation.” Journal of Big Data 2.1 (2015): 1-26.