Data Structure and Algorithm Design II
Chapter 10
Xingang (Ian) Fang
Sections
Dynamic Programming
Max Sum Subarray Problem
Chain Matrix Multiplication Problem
Longest Common Subsequence Problem
Dynamic Programming
Xingang (Ian) Fang
Overview
An algorithmic paradigm
Break into overlapping subproblems
Only calculate once to avoid repeated work
Store the result in a table for future use
Characteristics
What makes a problem suitable for dynamic programming?
Optimal substructure
Overlapping subproblems
Implementation techniques:
Memoization/tabulation
Recursive formulation
Either top-down or bottom-up
Problems Solved by DP
Enumeration, decision or optimization types of problems
Fibonacci numbers
Max subarray sum (Kadane’s algorithm)
Matrix chain multiplication
Longest common subsequence
Knapsack problem
Integer partition
Coin change
Rod cutting
Benefit and Challenges
Benefits
Optimal solution
Efficiency
Versatility
Clarity
Challenges
Memory usage
Identifying subproblems
Algorithm design
Time complexity
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
Number of distinct subproblems
Work per subproblem
Memoization/tabulation overhead
Recursive call overhead (top-down approach)
Space Complexity
Memorization table size
Call stack space (top-down approach)
Max Sum Subarray
Given an array of integers, find the contiguous subarray with the largest sum. The array can contain both negative and positive values.
For array \([-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]\), the contiguous subarray with the largest sum is \([4, -1, -2, 1, 5]\) with sum 7.
Many real-life applications
Stock market
Image processing
Bioinformatics
Problem type: Optimization
Need exact solution
Satisfies
Optimal substructure
Overlapping subproblems
Solutions
Brute-force \(\Theta(n^2)\)
Divide and conquer \(\Theta(n \log n)\)
Dynamic Programming (Kadane’s algorithm) \(\Theta(n)\)
Brute-force Solutions
Consider all possible subarrays and compute their sums
function brute_force_max_subarray(arr):
max_sum = -infinity
for start from 0 to length(arr) - 1:
sum_of_subarray = 0
for end from start to length(arr) - 1:
sum_of_subarray = sum_of_subarray + arr[end]
if sum_of_subarray > max_sum:
max_sum = sum_of_subarray
return max_sumDivide and Conquer Solution
Divide the array into two halves
Recursively find the maximum subarray sum in:
Left half
Right half
Crossing the midpoint
function max_subarray(arr, low, high):
if low == high:
return arr[low]
mid = (low + high) / 2
return max(max_subarray(arr, low, mid),
max_subarray(arr, mid + 1, high),
max_crossing_sum(arr, low, mid, high))Divide and Conquer Solution (cont.)
function max_crossing_sum(arr, low, mid, high):
left_sum = -infinity
sum = 0
for i from mid downto low:
sum = sum + arr[i]
if sum > left_sum:
left_sum = sum
right_sum = -infinity
sum = 0
for j from mid + 1 to high:
sum = sum + arr[j]
if sum > right_sum:
right_sum = sum
return left_sum + right_sumDynamic Programming Solution
Kadane’s algorithm
Idea: Compute the maximum subarray sum ending at each position
At each end position, the maximum subarray sum is either:
The maximum subarray sum ending at the previous position plus the current element
The current element
Scan the array from left to right only once
Dynamic Programming Solution (cont.)
Consider the array \([-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4]\):
Start with \(current\_max = arr[0] = -2\) and \(global\_max = -2\).
At the second element (1), \(current\_max\) is \(max(-2+1, 1)\), which is 1. \(global\_max\) is now \(max(-2, 1)\), which is 1.
This process continues, updating \(current\_max\) and \(global\_max\) with each new element.
By the end of the array, \(global\_max\) contains the maximum sum, which in this case is 6 from the subarray \([4, -1, 2, 1]\).
Dynamic Programming Solution (cont.)
function kadane_algorithm(arr):
current_max = global_max = arr[0]
for index from 1 to length(arr) - 1:
current_max = max(arr[index], current_max + arr[index])
global_max = max(global_max, current_max)
return global_maxChain Matrix Multiplication Problem
Overview
Given a sequence of matrices, find the most efficient way to multiply these matrices together.
The costs are different depending on how you associate the matrices in the multiplication.
Problem type: Optimization
Need exact solution
Satisfies
Optimal substructure
Overlapping subproblems
Solutions
Brute force
Dynamic programming
Example
Consider the multiplication of four matrices A, B, C, and D with dimensions \(10 \times 30\), \(30 \times 5\), \(5 \times 60\), and \(60 \times 10\), respectively. We can fully parenthesize the product in five distinct ways:
\(((AB)C)D\)
\((A(BC))D\)
\((AB)(CD)\)
\(A((BC)D)\)
\(A(B(CD))\)
The cost of 3 is the best:
\((10 \times 30 \times 5) + (10 \times 5 \times 60) + (10 \times 60 \times 10) = 1500 + 3000 + 6000 = 10500\)
\((30 \times 5 \times 60) + (10 \times 30 \times 60) + (10 \times 60 \times 10) = 9000 + 18000 + 6000 = 33000\)
\((10 \times 30 \times 5) + (5 \times 60 \times 10) + (10 \times 5 \times 10) = 1500 + 3000 + 500 = 5000\)
\((30 \times 5 \times 60) + (30 \times 60 \times 10) + (10 \times 30 \times 10) = 9000 + 18000 + 3000 = 30000\)
\((5 \times 60 \times 10) + (30 \times 5 \times 10) + (10 \times 30 \times 10) = 3000 + 1500 + 3000 = 7500\)
Brute Force Solution
The combinatorics: The way to parenthesize a product of \(n\) matrices is \(\Theta(\frac{4^n}{n^{3/2}\sqrt{\pi}})\). A.k.a. the Catalan number.
The complexity is close to exponent complexity.
The algorithm is not practical.
Dynamic Programming Solution
Bottom-up approach
Let the length of chain \(L\) range from 2 to \(n\).
Enumerate all subchains of length \(L\) in the sequence.
Enumerate all possible ways of parenthesizing each subchain by splitting the subchain into two subchains.
Time complexity: \(\Theta(n^3)\)
Memorization using two tables
\(m[i, j]\): The minimum number of scalar multiplications needed to compute the matrix \(A_i \cdots A_j\).
\(s[i, j]\): The index \(k\) at which we split the product \(A_i \cdots A_j\) in an optimal parenthesization \(A_i \cdots A_k A_{k+1} \cdots A_j\).
Both \(\Theta(n^2)\) space.
Dynamic Programming Algorithm (cont.)
C++ example that only computes the cost
int matrixChainOrder(int p[], int n) {
int m[n][n];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
m[i][i] = 0;
// L is the chain length
for (int L = 2; L < n; L++) {
for (int i = 1; i < n - L + 1; i++) {
int j = i + L - 1;
m[i][j] = INT_MAX;
// Try all possible split points
for (int k = i; k <= j - 1; k++) {
int q = m[i][k] + m[k + 1][j] + p[i - 1] * p[k] * p[j];
if (q < m[i][j])
m[i][j] = q;
}
}
}
// Return the minimum number of scalar multiplications needed
// to multiply the original chain
return m[1][n - 1];
}Longest Common Subsequence (LCS) Problem
Sequences and subsequences: foundational concepts in computational problems
Critical for sequence comparison in bioinformatics and computer science
DNA sequence alignment
DNA sequence similarity
Text comparison and plagiarism detection
File comparison
Version control systems
LCS Problem Overview
LCS: finding the longest subsequence common to two sequences
More than one possible solution
Subsequence: not necessarily contiguous
Used in genetics and version control systems
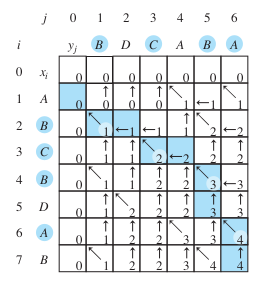
Example: The Longest Common Subsequence for the DNA sequences “AGGTAB” and “GXTXAYB” is “GGTAB”
LCS Problem Properties
Optimal Substructure: (last character match version)
For sequences X and Y, if X[m] equals Y[n], the LCS includes X[m] and is one more than LCS(X[1..m-1], Y[1..n-1]).
E.g. LCS(“ABCBDAB”, “BDCABB”) = 1 + LCS(“ABCBDA”, “BDCAB”)
If X[m] does not equal Y[n], the LCS is the longer of LCS(X[1..m], Y[1..n-1]) or LCS(X[1..m-1], Y[1..n]).
E.g. LCS(“ABCBDAB”, “BDCABD”) = max(LCS(“ABCBDAB”, “BDCAB”), LCS(“ABCBDA”, “BDCABD”))
Overlapping Subproblems:
Calculating LCS(X[1..m], Y[1..n]) will often require recalculating LCS(X[1..m-1], Y[1..n-1]), LCS(X[1..m], Y[1..n-1]), and LCS(X[1..m-1], Y[1..n]) multiple times.
Brute Force Approach
Involves comparing all possible subsequences of both strings and compare
Results in exponential time complexity \(2^{m+n}\)
Not feasible for long sequences due to inefficiency
Divide and Conquer Approach
Employ the subproblem definition of LCS
Recursively divide the problem into smaller subproblems
Redundant computations on overlapping subproblems
function findLCSLength(s1, s2, m, n):
// Base case: If either of the strings is empty, LCS length is 0
if m == 0 or n == 0:
return 0
// If the last characters of both strings match
if s1[m-1] == s2[n-1]:
return 1 + findLCSLength(s1, s2, m-1, n-1)
// If the last characters of both strings don't match
return max(findLCSLength(s1, s2, m, n-1), findLCSLength(s1, s2, m-1, n))Dynamic Programming (DP) Solution
DP Table: set up with dimensions one greater than sequence lengths
Matching characters: increment LCS length
Non-matching characters: take the maximum value from adjacent cells
LCS length located at dp[m][n]
Algorithm complexity: \(\Theta(m*n)\) for both time and space
Traceback for LCS
Can only find one LCS
Reconstruct LCS from the filled DP table
Backtrack from dp[m][n], storing characters
Diagonal movement for matches; otherwise to cell with higher value; if same, go up
Complexity: \(\Theta(m+n)\)
Question: How about same values?
Pseudocode
Function LCS(X, Y):
m = length of X
n = length of Y
dp = array of (m+1) rows and (n+1) columns
# Initialize the table with 0's, as the LCS of an empty sequence
# with any sequence is 0
For i from 0 to m:
dp[i][0] = 0
For j from 0 to n:
dp[0][j] = 0
# Fill the dp table
For i from 1 to m:
For j from 1 to n:
If X[i] == Y[j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
Else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
# The length of LCS is in the cell dp[m][n]
length_LCS = dp[m][n]Pseudocode (cont.)
# To find the LCS string, traceback from dp[m][n]
LCS = ""
i = m, j = n
While i > 0 and j > 0:
If X[i] == Y[j]:
LCS = X[i] + LCS # Prepend the character to LCS
i = i - 1
j = j - 1
Else If dp[i-1][j] >= dp[i][j-1]: # if same, go up
i = i - 1
Else:
j = j - 1
Return LCS, length_LCSVariations
All LCSs: The DP solution only finds one LCS. To find all LCSs, use backtracking to find all possible paths in the DP table that lead to the LCS length.
Longest Common Substring: A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string. The Longest Common Substring (LCSu) problem is similar to the LCS problem, but requires that the common elements be contiguous.
Improve space complexity: The DP solution requires \(\Theta(m*n)\) space. This can be improved to \(\Theta(min(m, n))\) by only storing the current and previous rows of the DP table.